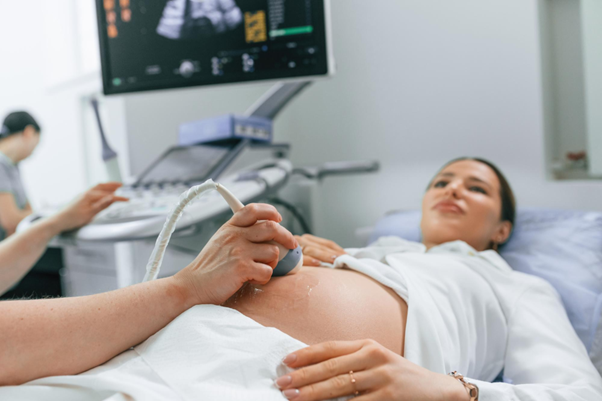
Sonograms, also known as ultrasound scans, are essential tools in healthcare that use sound waves to create images of the body's internal structures. Unlike X-rays, sonograms do not use radiation, making them safe and widely used for various medical purposes
What is a Sonogram?
A sonogram is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create pictures of organs, tissues, and blood flow inside the body. It's commonly used during pregnancy to monitor foetal development and for diagnosing medical conditions in other parts of the body.
Uses of Sonograms
Sonograms have many uses in medicine:
- Obstetrics: Monitoring the growth and health of a baby during pregnancy.
- Abdominal Imaging: Checking organs like the liver, kidneys, and bladder.
- Cardiac Imaging: Assessing the heart's structure and how well it works.
- Musculoskeletal Imaging: Examining muscles, tendons, ligaments, and joints.
- Vascular Imaging: Evaluating blood flow and finding issues in blood vessels.
Types of Sonograms
Different types are used based on what part of the body needs to be checked:
- Transabdominal Ultrasound: For organs in the belly area and monitoring pregnancies.
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: Gives detailed images of the uterus and ovaries.
- Doppler Ultrasound: Checks blood flow in vessels and the heart.
- Echocardiography: Focuses on the heart's structure and function.
- Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Looks at muscles, tendons, and joints for injuries.
How Sonograms Work
During a sonogram, a small device called a transducer is moved over the skin with gel. It sends sound waves into the body, which bounce back as echoes from organs and tissues. These echoes make real-time images shown on a screen. It's painless and usually takes 30 minutes to an hour, depending on what's being looked at.
What to Expect During a Sonogram
- Preparation: Sometimes you'll need to fast or drink water before the scan.
- Procedure: You lie down, and the technician moves the transducer over your skin to capture images.
- Afterwards: You can go back to your normal activities. The results are discussed with your doctor later.
Benefits of Sonograms
- Non-invasive: Safe because it doesn't use radiation, so it's okay for pregnant women and can be used many times.
- Real-Time Images: Shows doctors what's happening right away, so they can decide on treatment quickly.
- Versatile: Used in different medical fields to see inside the body clearly.
Whether it's to check on a baby's growth or to look at organs, sonograms help doctors understand what's happening inside your body. Knowing how they work and why they're used can help you feel more comfortable if you need one. If you have questions or are getting a sonogram soon, understanding its benefits will help you feel more at ease and get the best care possible.